Methodology, Tools, and Guidelines on Forecast-Based Financing (FBF) for Mongolian Context
Prepared by : Z M Sajjadul Islam, UNDP-International Consultant
Acronym
| ALAGaC/ | Administration of Land Affairs, Geodesy, and Cartography |
| ALAMGaC | Agency for Land Administration and Management, Geodesy, and Cartography |
| AWS | Automatic Weather Station |
| 5W | Who will do what, where, when, and how |
| BTS | Base transceiver station |
| CRVA | climate risk and vulnerability assessment |
| CSV Excel file | comma-separated values |
| CAP | Common Alerting Protocol |
| CBO/CSO | Community-based organizations / Community services organizations |
| IBFWS | Impact-based Forecast and Warning Services |
| CRVA | Climate Risk and Vulnerability Assessment |
| DIMA | National Rangeland Monitoring Database |
| EM-DAT | Emergency Events Database |
| DCPC | Data Collection and Processing Center |
| DTM/DEM | Digital Terrain Models (DTM)/ Digital Elevation Models (DEM) |
| EAP | early action protocol |
| EOC | Emergency Operations Center |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| AM/FM Radio | Amplitude Modulation/Frequency Modulation |
| FBF | forecast based Financing |
| FGD | Focus Group Discussion |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| HCT | Humanitarian Country Team |
| HPC | high processing power computing |
| IBF | impact-based forecasting |
| ICS | Incidence Command System |
| ICT | Information and Communication Technology |
| IFRC | International Federation of Red Cross and Red |
| IM | Information Management |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| I-NGOs | International /National Non-Governmental Organization |
| IRIMHE | Information and Research Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology, and Environment |
| IVR | Interactive Voice Response |
| KII | Key Informant Interviews |
| KML/KMZ | Keyhole Markup Language |
| LEMA | Local Emergency Management Agency |
| L & D | Loss and Damage |
| MET | Ministry of Environment and Tourism |
| MIS | Management Information System |
| MHEWS | multi-hazard early warning system |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| MoED | Ministry of Economy and Development |
| MOU | Memorandum of understanding |
| MoFALI | Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Light Industry |
| MRCS | Mongolian Red Cross Society |
| NAMEM | National Agency Meteorology and the Environmental Monitoring |
| NEC | National Emergency Commission |
| NEMA | National Emergency Management Agency |
| NMHS | National Meteorological and Hydrological Services |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| ODBC/JDBC | Open Database Connectivity/ Java Database Connectivity |
| PDNA | post-disaster damage, loss and needs assessment |
| NSO | National statistics office |
| PIU | Project Implementation Unit |
| PSTN | Public switched telephone network |
| RIMES | Regional Integrated Early Warning System for Africa and Asia |
| R & D | Research & Development |
| SMS | Short Message/Messaging Service |
| SEC | State Emergency Commission |
| SME | Small and Medium Enterprise |
| SoD | standing orders on disaster |
| SOP | Standard Operating Procedures |
| TWG | Technical Working Group |
| WCS | Web Coverage Services |
| WMS | Web Map Service |
| WFS | Web Feature Service |
| WPS | Web programming service |
| UHF | Ultra-high frequency |
| UNDP | United Nations Development Programme |
| UNEP | United Nations Environment Programme |
| UNFPA | United Nations Population Fund |
| UNICEF | United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund |
| VHF | Very high frequency |
| WFP | UN World Food Program |
| WMO | World Meteorological Organization |
Contents
1.1 Rationale Forecast-based financing (FBF) 5
1.2 Development of centralized dashboard for the FBF decision-making process. 5
1.5 Rationalizing IFB-driven FBF. 7
1.6 IBF driven forecast-based risk financing (FBF) mechanism for Mongolia. 8
2.0 Stakeholder Partnership Coordination and Engagement 9
2.4 Functions of leading partners for the FBF Process. 12
3.0 Risk Finance Planning & decision-making dashboard. 14
3.1 IBF Driven FBF decision-making mechanism.. 15
4.0 Forecast based Financing (FBF) Process. 22
4.1 FBF framework approach. 23
4.3 IBF integrated FBF approach for DRR. 24
4.4 FBF risk consideration approach & Readiness for Climate Risk Finance Mobilization. 25
5.0 Methodology for Developing Early Action Protocol ( EAP) 27
5.1 Define types of EAP and Functions: 27
5.2 Team composition for developing EAP and early warning based early actions : 29
5.3 Steps of Developing EAP. 30
5.4 Developing EAP for managing season-specific and combined dzud risks. 33
6.0 Early Warning and Early Action for the rapid onset events. 35
6.1 Early Warning and Early Action : 35
6.2 Developing Forecast based early Action : 35
6.3 Anticipatory Actions for Copping the Rapid Onset Hazards. 36
7.0 FBF strategy development for the vulnerable sectors. 38
7.1 : IBF integrated informed FBF tool supporting long-term planning. 38
1.0 Introduction: Forecast-Based Financing (FBF) Mechanism
Forecast-based Financing (FBF) is a risk financing mechanism informed by the weather and climate emergencies that are likely to be impending over the high-value elements and having the likelihood of doing the Losses and damages( L & D) beforehand it needs to be well-informed, anticipated, and immediate actions are undertaken to minimize the L & Ds. The FBF critically depends on precision-level forecasting & early warning, anticipatory early action, and early action protocol (EAP). The FBF process needs to be triggered automatically by the integrated weather warning, alerting, multi-hazard early warning, and Impact-based forecasting(IBF) system being operational at met-agency in the wake of climate extreme weather events that are likely to be impending over the ground based on frequency, intensity, and ripple effects of hazards over the days/weeks/months. Therefore integrated IBF and FBF system design encompasses ICT/IT system architecture (informed geospatial tools, IT database of ground level elements, the IT system induced impacts calculation over the medium-high value elements, categorizing elements that are likely to be impacted ) that can automatically estimate anticipatory L & D are likely by the early warning being issues with spatiotemporal scale. The IBF integrated FBF essentially needs to instrumentalize the national disaster management organization (NDMO) at the country level to activate EAP, forecast-based early humanitarian action timely and mobilizing the disaster risk finances e.g, Central Emergency Response Fund, disaster emergency response funds, UN-track funds, national disaster management disaster emergency response funds, etc., for humanitarian response and climate crises to minimize the L & D. However, in the normal circumstances the inclusive risk financing decision-making process can be undertaken based on EAP / forecast based early action for slow-onset multi-hazards are likely to be impending and necessarily ex-ante and ex-post financing for mitigating the climate risks.
The multi-modal risk finances and fiscal mobilization for forecast-based financing, disaster emergency response management, and climate crisis management require informed and evidence-based decision support tools essentially for quantifiable needs put in place before crises start. The process is being tangled by the lingering bureaucratic process to conduct much-needed and life-saving humanitarian assistance.
1.1 Rationale Forecast-based financing (FBF)
Risk-informed local development planning and finance decision-making in normal circumstances entails concerted effort which comes across inclusive participation of all relevant stakeholders (engagement of governments and duty-bearers, stakeholders, donors, I-NGOs, sector departments, financial institutions, insurers, credit operators, vulnerable community, etc.) and agreed consensus. The rollout of climate and disaster risk financing instruments is urgently needed to enable governments and the humanitarian sector to strengthen SafetyNet for the most vulnerable and provide timely financing and assistance. However, the rapid-onset extreme weather events and compounding hydrometeorological hazards, geological hazards induced by extreme weather events financial crises, and pandemics, are increasingly exerting daunting challenges to the government’s abilities to manage climate risks at the large scale to initiate efforts to protect the lives, livelihood,s and assets from impending hazards, and the stakeholders/actors essentially need early warning informed and bad weather forecast based anticipatory early action ( risk finances and humanitarian preparedness) before hazards turning to disaster minimizing the human tolls and L & Ds. Operationalizing the FBF mechanism can effectively support needs-based early actions to get the climate frontline well prepared for climate extremes to minimize the L & Ds.
Due to global climate perturbation, extreme weather events are impending as the fastest onset with higher intensities & frequencies and significantly doing loss and damage to the climate frontlines. Improved access to weather information services is now highly demanded by the climate frontlines. Robust observation mechanisms, precision level numerical weather predictions, weather warnings, and multi-hazard early warning systems are indispensable tools for making informed decisions effective at the critical juncture of humanitarian preparedness and response planning at the advent of hazardous impending weather being forecasted over the shortest lead time to prepare for the frontline community for strengthening the withstanding capacity against the impending triggers/hazards that could potentially turn into a disaster and loss and damage are highly likely.
The robust ICT-enabled FBF mechanism is the output of service delivery which comes across multiple and recurrent processes in the background. The FBF process to invoke while national meteorological and hydrological services (NMHS) issue impact forecasts (triggers) through impact-based forecast platforms e.g., thresholds of impacts, level of early warnings, special alerts, and calculated anticipatory loss and damage of impending hazardous events combined.
The FBF mechanism enables the humanitarian program cycle to access humanitarian funding for early action informed by the impact-based forecast (IBF) on impending extreme weather effects, impact level, risk, vulnerabilities, loss, and damage likely. FBF aims to anticipate disasters, prevent their impact, if possible, and reduce human suffering and losses.
1.2 Development of a centralized dashboard for the FBF decision-making process.
- Setting up a centralized informed Dashboard for visualizing impending multi-hazards, persistent trends of multi-hazards over the ground already experienced, hazardous weather events, proposed high-value elements (City, township, settlements, built-up installations/infrastructures, basic service delivery installations/facilities, key & Critical service delivery installations/facilities) are likely to be impacted, determining what are the effective early action protocol (EAP) being required for early preparedness of every extreme event, what are the early action plannings are required for rapidly addressing the crises and finally what would be inclusive risk-finances are being needed for early mobilizing and early preparedness so that impacts level and L & Ds can effectively be minimized.
- IBF integrated FBF can essentially support the NDMO to come up with quick-time-around inclusive and concerted actionable early action planning participated by the stakeholders(stakeholders, sector departments, other grassroots level state & non-state actors, private sectors, risk-financiers, climate frontlines ) for sectoral level early action protocol development, humanitarian response planning, and sectoral climate action planning and inclusive risk finance allocation and mobilization decision making.
- FBF decision support system to facilitate stakeholders in Hazard/climate crisis-specific inclusive and timely trigger emergency responses, humanitarian assistance and risk mitigation planning, and resource mobilization
- Informed IBF/FBF dashboard-driven informed tools can support Ex-ante and Ex-post financing mechanisms for grand barging with donors/financial institutions, and private sectors, propagation of risk-financing policy, planning & advocacy for optimizing the risk-finance mobilization drives at the internal and external level for addressing slow-onset climate crises.
- FBF Informed tools for facilitating Grand bargaining with donors about the niche demand and optimal uses of risks finances.
- FBF Informed tools supported mixed mode & financing co-financing modality for addressing the slow and medium onset climate crisis.
- Optimum uses of climate risk finances for timely disbursement and undertaking climate actions
1.3 Objective :
The core elements of FbF to inform weather & climate risk-integrated planning decision supports for the allocation of financial resources are agreed upon in advance, together with the specific forecast threshold(triggers) and allocatable resources for the implementation of early actions. The roles and responsibilities of everyone involved in implementing these actions are defined in the Early Action Protocol (EAP), and Early warning-based early action planning. This ensures full commitment to implementation among the involved stakeholders.
1.4 Overview of FBF
The implementation of the intended FBF mechanism to address the Mongolian disaster emergency management over to comprehensively supporting humanitarian program cycles IBF-driven FBF to inform the scenario setting of what consequences are likely ahead of impending hazards before interacting with the ground. The emergency risk management and critical finance decision-making process depend on the informed tools and the quick-time-around scenario overviews of impending extreme weather events. IBF integrated FBF dashboard intended to support the timely execution of early warning advisory-based on early action, early action planning, contingency planning, disaster emergency preparedness planning and finance mobilization, etc. The evidence-based risk-informed (IBF supplied) decision support tools are essential to mechanize the bureaucratic process for fostering the grand bargains/advocacy with the climate & humanitarian risk financing community for timely mobilization of risk finance to meet the climate crises ahead of impending. Informed tools supported FBF mechanism would be also able to enable stakeholder policy and planning coherence, inclusive-participatory, and self-esteemed multi-stakeholder coordinated participation to risk financing and response to crises.
Day by day climate emergencies are turning to rapid onset patterns and fundamentally the traditional risk management paradigm is gradually becoming ineffective. The new methodology and tools for IBF-informed FBF are intended to meet climate emergencies robustly.
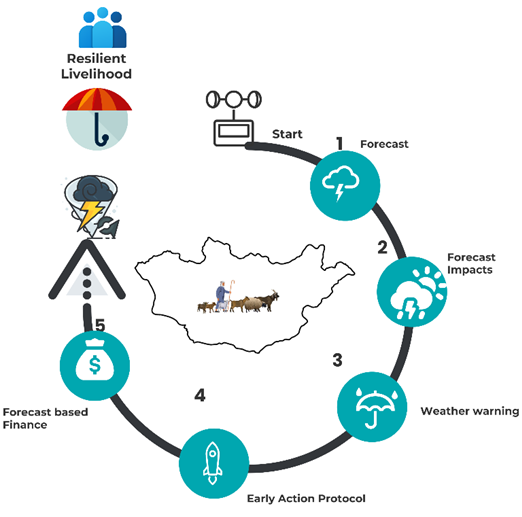
Figure 1: FBF work flow diagram
The traditional climate and multi-hazard risk financing limited to relief and in-kind support mobilization. However, the IBF informed FBF process to be enabled to leverage the financing instruments for the humanitarian community to plan contingencies for preparedness in the advent of impending multi-hazards and post-disaster response planning for the frontline community to be better prepared ahead of forecasted impending hazards likely the loss and damages and to understand the impact level minimizing the L & D.
However, the IBF driven FBF an excellent leverage for the humanitarian program cycle ahead of disaster strikes being always faces critical challenges in terms of number of the population are likely to be impacting, magnitude, the threshold of trails of disasters, assessment and summing up anticipatory L & D , what would be the preparedness for the frontline vulnerable community, forecast-based early action planning, contingency preparation, timely pre-positioning relief items to the doorstep of the vulnerable community, etc., so that loss and damage could be minimized to as lowest as possible.
The dashboard informed IBF can sufficiently meet the humanitarian decision making process with the evidence-based and ICT-driven tools can represent the clear picture of where the extreme and hazardous weather event induced impact thresholds are spanning, and exactly how many elements are likely to be impacted based on forecasted extreme weather thresholds. As a result, the national and local government efforts remain challenged to formulate demand-driven contingency planning for the target group and location, prepositioning emergency relief items (types and amount), cash grants, and in-kind support to be prioritizing and essentially to mobilize the most vulnerable areas and hard to reach areas for better preparedness.
1.5 Rationalizing IFB-driven FBF.
The FbF process is another outset of the whole climate emergency management process in which the system needs to essentially inform the stakeholders about the risk-informed tools and mandate the inclusive financing mechanism being well incorporated with the whole value chain. We understand disaster emergency risk management is such a time-critical response management process that needs to come across over the quick disposal of decision-making process over the government bureaucratic channel within a short time span otherwise response cannot be mobilized at the point of crisis, effectively and efficiently, and L & D would be the larger extent.
However, integrated IBF & FBF are intended to represent an informed tool driven, evidence-based grand bargaining instrument being intended objectively to drive foster, self-esteemed, empirically fastening the political and bureaucratic decisions making process which would be supportive to address the onset of climate/weather emergencies, and to planning and mobilizing resources for addressing disaster emergencies, so that quick -time-around decisions can be made to save lives, and properties and getting vulnerable sectors & elements well prepared for the impending hazards.
IBF and concurrent FBF are being attempted to remove the planning and decision-making barriers, creating enabling and coherent coordination mechanism that enables access for funding, planning early action, contingencies, and mobilizing resources for risk preparedness at local level.
1.6 IBF driven forecast-based risk financing (FBF) mechanism for Mongolia.
The whole risk financing mechanism to address the climate risk and crises, impeding hazards, and potential disasters are likely to do damage. The perspective of weather extreme and impending multi-hazards in Mongolia are varying. The risk finance instrument should be aligned with the need-based risk management and deliverability for sustaining actions from national to local to the frontline vulnerable community level.
The persistent climate risk and vulnerability patterns over the Mongolian landscape are recurrently varying over the geographical, landscape, landform, landcover, environmental, and hydrometeorological settings. Additionally, the impending hazardous weather events are also heavily spatiotemporally impactful, and while those events are interacting with the ground-level elements the impact levels also vary from place to place. Considering the variability patterns of both the weather system and landscape – a suitable IBF methodology (proposed) and corresponding FBF methodology and informed tools are also intended.
Informing the whole risk management mechanism, Mongolia needs a variety of impact forecasts for tacking both hazardous weather and good weather whatever is impending and interacting over the grounds. An integrated IBF and FBF are instrumentalized and intended to support the whole spectrum of government climate crisis management strategies. The proposed IBF has a multi-faceted capacity to inform government and stakeholders policy and planning desk for supporting risk management planning, strategies, action planning, program and project design, implementation, and monitoring, etc.
The whole IBF partnership and workflow is mandated to support all demand-driven IBF and FBF. The risk information service upgradation and demand are mounting at pace with climate crises.
2.0 Stakeholder Partnership Coordination and Engagement
2.1 Core objective:
- Ensuring inclusive participation of stakeholders (state, non-state, and development partners ) in risk-informed early action protocol development and strategy for forecast-based financing (FBF).
- Supporting sector ministry & departments in risk-informed intervention development and inclusive budgeting & financing for better preparedness against the impending different onset extreme weather invents and multi-hazards.
- Establishing an integrated & inclusive financing mechanism being heavily informed by Impact forecast, early warnings ( multi-hazards) likely to impend, persisting risk & vulnerabilities, and evidence-based risk financing modality development. Ensure optimized utilization of risk finance by avoiding overarching and duplication of interventions and recurrently giving equal importance to hard-to-reach areas.
2.2 FBF Framework approach:
Addressing the impending multi-hazards ( slow onset, medium onset, and rapid onset ) risk and vulnerabilities, Mongolia needs a multi-modal risk financing mechanism to address different types of multi-hazards. For the detection of diverse and rapidly changing weather phenomena, an impact forecasting and integrated impact-based forecasting (IBF) methodology is already being proposed. Back-to-back IBF informed FBF intended to inform emergency hazard management agencies, humanitarian actors, and sector departments about how to develop early warning-based early action plans (contingency & preparedness) to act before disasters to minimize the socio-economic costs of impending weather and climate hazards.
Multi-stakeholder, vulnerable sectors, relevant organizations, frontline herders, vulnerable communities, and individuals can make critical decisions to ensure that resources and supplies are in place to take early action and to respond as soon as it is safe to do so. IBF-supported FBF plays an important role in facilitating Red Cross Red Crescent running Forecast-based finance Mobilization, early action planning, and preparedness.
It is however a critical job over the very shortest spanning of a lead-time understandability of the anticipatory impacts, loss & damage, and scalability of impending extreme weather event(s) turning to multi-hazard(s) being just forecasted. IBF-supported FBF can play an important role in overcoming the difficulties relating to the anticipatory estimation of L & D, formulation of early warning-based early actions, detailed early action protocol (EAP), and contingencies for preparedness the forecast-based financing mechanism is essential for mitigating risk and vulnerabilities.
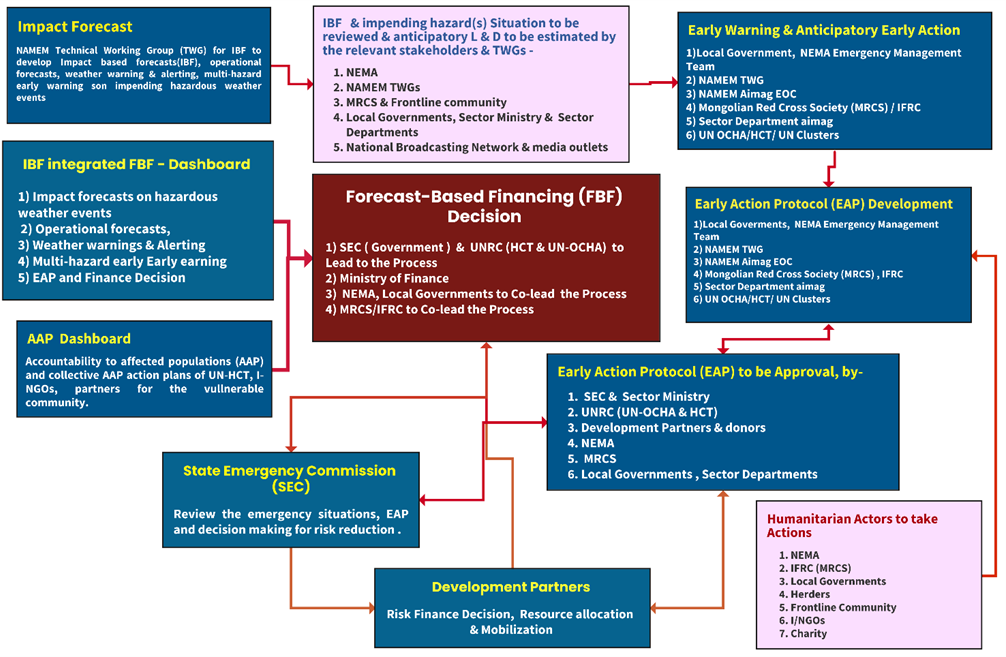
Figure 2: FBF decisions framework – governed by the partnership and functional coordination process (Source : Z M Sajjadul Islam )
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
For complete document, design, and installation of the FBF mechanism at the country level, please contact Z M Sajjadul Islam
Email : zmsajjad@gmail.com